
What is Middleware?
Middleware is software embedded in the app pipeline that processes requests and responses. ASP.NET Core provides a rich set of built-in middleware components, but in some scenarios, you may need to write custom middleware.
Let's see with a practical example
Learn how to create your own custom middleware and add it to your ASP.NET Core application's request pipeline.
A custom middleware component is like any other .NET class with an Invoke() method. However, the constructor needs her RequestDelegate type parameter to execute the following middlewares in order:
Visual Studio includes templates for creating standard middleware classes. To do this, right-click the project or folder where you want to create the middleware class and select Add -> New Item. This will open the Add New Item popup. In the top right search box, search for the word "middleware" as shown below.
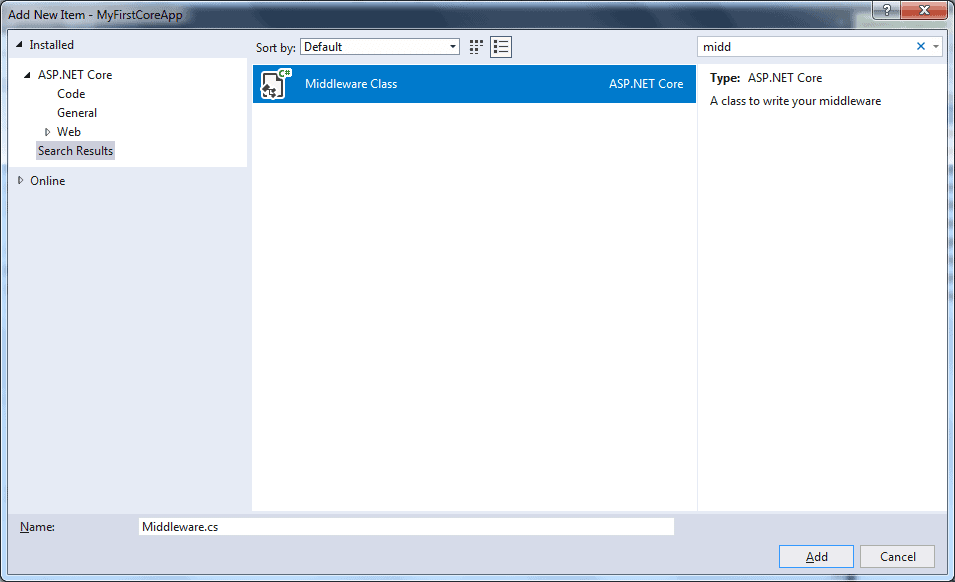
Select the class and give it a name and then click on Add.
This will look as shown below. (Middleware class added with extension method)
As mentioned above, the Invoke() method is not asynchronous. So change it to asynchronous and write your custom logic before calling next();
Add Custom Middleware
Next, we need to add our custom middleware to the request pipeline using an extension method as shown below.
Add Middleware into Request Pipeline:
You can also add middleware using the IApplicationBuilder 's app.UseMiddleware() method.
Therefore, you can add custom middleware to your ASP.NET Core application.
